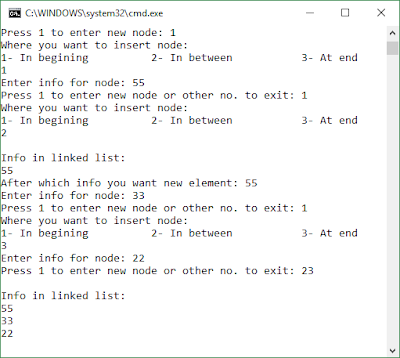
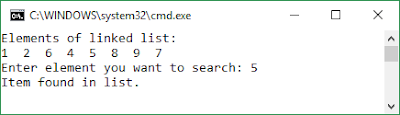
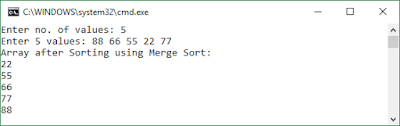
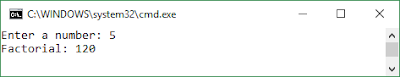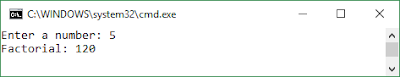In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers or Fibonacci sequence are the numbers in the following integer sequence:
01, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144.....
The Fibonacci spiral: an approximation of the golden spiral created by drawing circular arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling; this one uses squares of sizes 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, and 34.
By definition, the first two numbers in the Fibonacci sequence are either 1 and 1, or 0 and 1, depending on the chosen starting point of the sequence, and each subsequent number is the sum of the previous two.
Information source: wikipedia.org
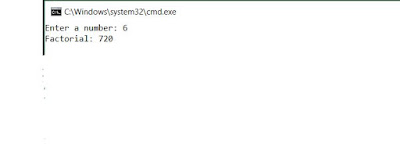
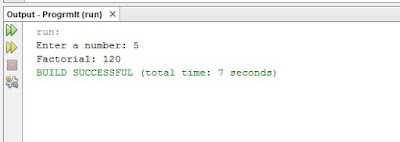
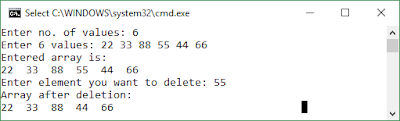
Program:->
 |
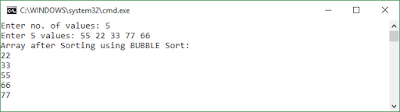
| Output |
def fibo( x ):
f = -1; s = 1
for i in range(0,x):
n = f + s
f = s
s = n
print n
return;
n = input ("Enter the total elements in the series: ")
print "The Fibonacci series is: "
fibo(n)
Read More >>